Table Of Content

The shaft—the part of the hair we see—is made up of dead cells and consists of three different layers. As a piece of hair grows, it goes through three phases before it sheds and a new one grows. Embedding melatonin under the skin of goats can increase cashmere production (18, 19). Melatonin can increase goat secondary follicle density and does not affect the growth of primary follicle density (18, 20).
Genes control curly hair
The follicle is the primary structure from which hair can grow. The histological arrangement of the follicle is divided into outer and inner root sheaths. The suprabulb region extends from the hair bulb to the isthmus and consists of components of the hair shaft, IRS, ORS, vitreous layer, and fibrous root sheath. The glossy (vitreous) layer is the eosinophilic acellular zone surrounding the ORS.
How It Gets Its Shape
The lower part of the dermal papilla is connected to the fibrous root sheet. The hair matrix surrounds the top and sides of the dermal papilla. In this chapter, the basic anatomy and the amazing and complicated biology of the hair follicle is reviewed.
Assignment of common scattering signals
They point outward and upward and interlock with the IRS cuticle, which leads to a firm attachment between the hair shaft and the IRS. As a result, they move upward in the follicular canal as a single unit. The first sign of catagen is the termination of melanogenesis in the hair bulb.
Architectural Niche Organization by LHX2 Is Linked to Hair Follicle Stem Cell Function - ScienceDirect.com
Architectural Niche Organization by LHX2 Is Linked to Hair Follicle Stem Cell Function.
Posted: Thu, 05 Sep 2013 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Hair Follicle Functions
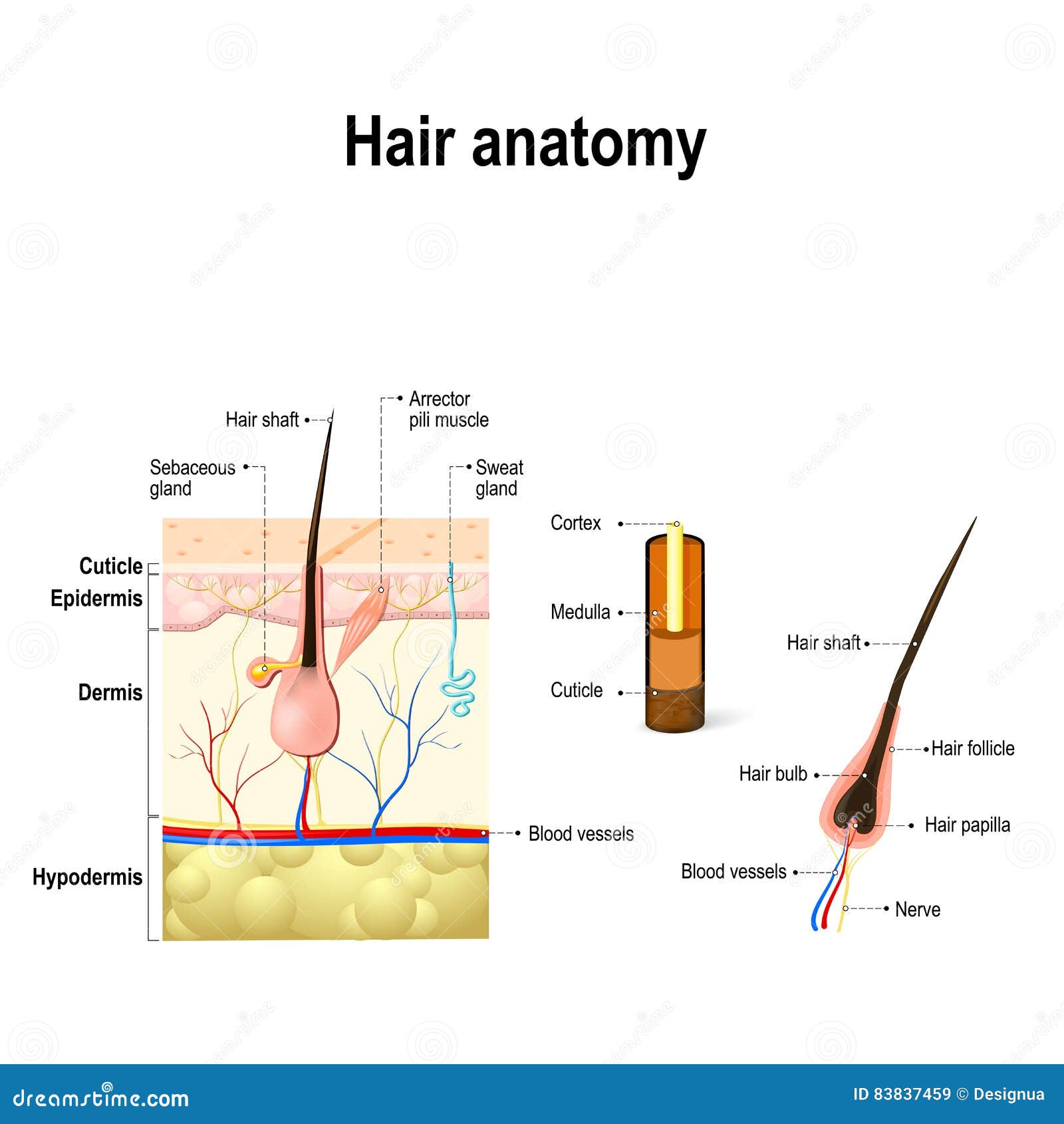
This can affect women too and is called female pattern baldness when it presents itself in women. Each strand of hair is made up of two separate structures. The first is the hair shaft, which comprises the visible part outside the skin, and the second is the hair follicle, which lies underneath the skin's surface.
As a person ages, the melanin production decreases, and hair tends to lose its color and becomes gray and/or white. The hair follicle is one of the characteristic features of mammals serves as a unique miniorgan (Figure 1). In humans, hair has various functions such as protection against external factors, sebum, apocrine sweat and pheromones production and thermoregulation.
Recent Findings with Computerized Methods for Scalp Hair Growth Measurements - ScienceDirect.com
Recent Findings with Computerized Methods for Scalp Hair Growth Measurements.
Posted: Fri, 22 Dec 2017 08:09:03 GMT [source]
A traditional meta-analysis was used to analyze hair follicle and litter size data. Specifically, primary and secondary hair follicle densities, cashmere yield, cashmere fiber length, and litter size were treated as continuous data. Using Review Manager (version 5.4), the meta-analysis was performed according to the random model.
How do I strengthen my hair follicles?
Identification and characterization of these features is an important step towards the detection of abnormalities in the molecular structure of hair as a potential diagnostic tool for certain diseases. Hair follicle melanocytes and their precursors reside in the hair matrix and along the outer root sheath of anagen hair follicles. However, production of hair pigment (black eumelanin and/or the reddish pheomelanin) only occurs in the specialized hair follicle pigmentary unit, located above and around the dermal papilla during anagen III–VI. Melanin synthesis is established in lysosome-related organelles named melanosomes.
Below the sebaceous duct, the hair and the follicular wall are intimately connected, however, above the duct, the hair becomes free in the intraepidermal pilary canal (Standring, 2016). In the deepest portion of the each hair follicle lies the hair bulb. It is supplied with nutrients via blood by a structure called the hair papilla.
As long as new hair cells continue to grow in the hair bulb, the hair continues to grow longer. At any point in time, about 90 percent of a person’s total amount of hair is in this growth phase. Above the dermal papilla is the hair matrix which consists of proliferating keratinocytes. These cells proliferate and gradually move upwards where they are keratinized to produce the hair shaft. The isthmus is the shortened segment of the hair follicle, extending from the attachment of the erector pili muscle (bulge region) into the entrance of the sebaceous gland duct.
Activation of this β-catenin pathway seems to be essential for the epithelial ability of the hair follicle production [7]. Androgenetic alopecia, which is known as male pattern baldness when it presents in men, is a condition that affects the growth cycle of hair follicles on the scalp. The hair cycle slows down and weakens, eventually stopping altogether.
Medullary cells contain glycogen-rich vacuoles and medullary granules, which contain citrulline (similar to the cells of the IRS). Hair follicles originate in the epidermis and have many different parts. Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing. Hair is present on almost the entire surface of our body, excluding certain regions such as the palms of our hands, soles of our feet, and some genital areas.
If you pull out a strand of hair, you might notice a bulb or round ball (root) attached to the end of the hair strand. The root is surrounded by nerve fibers that let you feel when your hair moves or you touch your hair. Removing this root doesn’t mean your hair won’t grow back, because in most cases, it will.
The Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) profile was well fit with three Gaussian peaks at 90 Å, 45 Å, and 27 Å. We note that the third peak was not observed in all hair samples. The corresponding peak positions and distributions are shown in the figure. The 90 Å peak has been reported early in the literature as the distance between intermediate filaments in human hair. Androgenetic alopecia is a widespread problem, and hair follicle growth studies are key to treating alopecia (39, 40). Melatonin may be a potential treatment for androgenetic alopecia (12).

No comments:
Post a Comment