Table Of Content
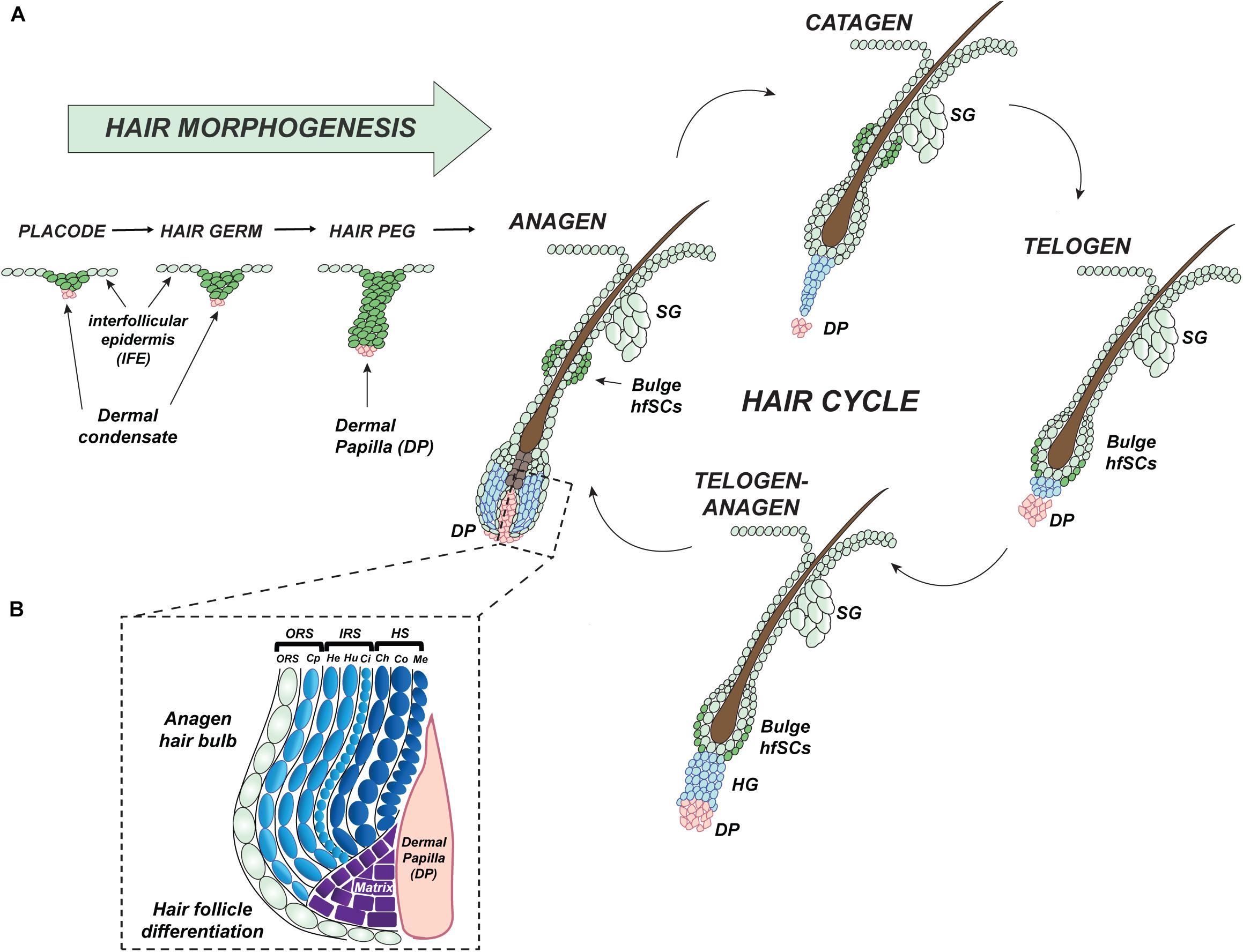
Approximately 84% of scalp hairs are in the anagen phase, 1-2% are in the catagen phase, and 10-15% are in the telogen phase. Cutaneous vascularization is provided by arterioles, which are concentrated at the lower portion of the hair follicle and compose vascular network. During the hair cycle phases, there are some alterations in the density of perifollicular vascularization due to the upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression [1]. Androgenetic alopecia is the most common presenting hair concern and affects 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States alone. Studies estimate that 70% of men and 40% of women are affected by androgenetic alopecia. Men will classically present with receding temporal hairlines, described as hair thinning and loss in an “M” shape.
Structure
A recipe for cyclical regeneration of bioengineered hair - riken.jp
A recipe for cyclical regeneration of bioengineered hair.
Posted: Wed, 10 Feb 2021 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The muscle will contract in cold temperatures, which causes the hair to orient vertically. Finally, the inferior segment forms the remainder of the deep hair follicle and expands to form the hair bulb. At the base of the bulb is the dermal papilla that provides vital blood supply to the growing hair follicle. The dermal papilla appears as an invagination of dermal connective tissue upward into the epidermis-derived hair follicle.
1. Hair growth cycle
FGF5 is a key inducer of catagen and FGF5-deficient mice have a prolonged anagen phase. In addition to FGF5, TGF-β1, IL-1b, the neurotrophins NT-3, NT-4 and BMP2/4 and TNF-α have been described to induce catagen [36]. The volume and secretory activity of follicular papilla and also the number of matrix stem cells determine the size of the anagen hair bulb, the duration of anagen phase and the diameter of the hair shaft [11, 26, 27]. Moreover the follicular papilla is an essential source of growth factors [1, 3, 16, 28]. 5 and and6,6, we identify three features present in all individuals.
What is the function of a hair follicle?
It is important to diagnose hair disease correctly, as the treatment for hair loss is dependent on the diagnosis. Once the hair follicle has developed in the fetus, lanugo hairs grow in utero. They eventually shed by about 36 to 40 weeks gestation and are replaced by vellus hairs that cover most areas of the body. Meanwhile, thicker, courser terminal hairs can be found on the head in certain areas such as the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
Melatonin affects hair regeneration
On average, your hair grows about half an inch each month. Your hair growth rate can be affected by your age, hair type, and your overall health. You can’t pull out a hair follicle, as it’s the structure within your skin that holds your hair.
The catagen phase begins with the end of the anagen phase and is characterized by a transition into quiescence. During this phase, which can last a few weeks, the hair follicle undergoes apoptosis-driven regression and loses about one-sixth of its standard diameter. The formation of a club hair, an important prognostic indicator in assessing hair pathology, also occurs at this time. If many hairs form club hair at once and are subsequently shed, it can give the appearance of thinning. Some conditions this may occur in include, but are not limited to, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, stress, vitamin deficiencies, and post-childbirth.
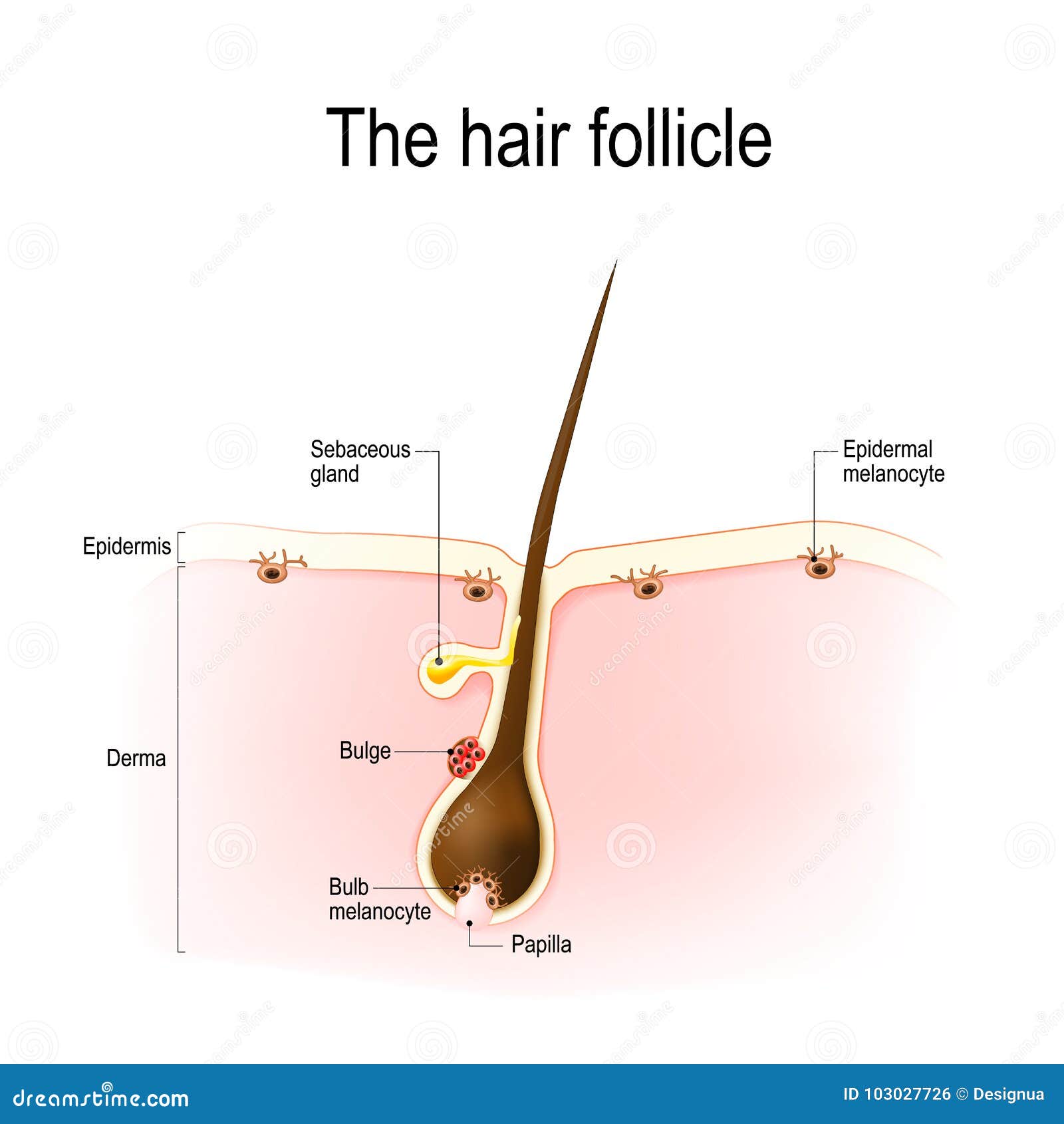
Hair structure
Additionally, the hair follicle contains an inner and outer root sheath. The size of hair follicles varies considerably during the existence of the follicles. Anagen hairs vary in size from large terminal hairs, such as those on the scalp, to the small vellus hairs that cover almost the entire glabrous skin (except palms and soles). Under hormonal influences, the vellus hair follicles in the male beard area usually thicken and darken at puberty.
If the data were in figures, the GetData Graph Digitizer (version 2.26) was used to obtain the data (23). When extracting data of melatonin’s effect on gene expression, only the genes mentioned in the study were obtained and the data uploaded to the database were not used. ● Melatonin did not affect goat primary follicle and litter size.
Hair loss can also refer to apparent hairlessness, which a clinician will elicit by asking if the patient notices areas without hair or regions where hair seems to be less thick or provide less coverage. Teasing out this distinction is necessary to determine the correct diagnosis. Hair follicles are made up of many different components, but these are the four key structures. Some people have curly corkscrew hair, while others have thick, straight, shiny hair.
This feature is also useful for the detection of the presence of insects or other potentially damaging substances on the skin surface. This is visible in humans as goose bumps and even more obvious in animals, such as when a frightened cat raises its fur. Of course, this is much more obvious in organisms with a heavier coat than most humans, such as dogs and cats. Outer root sheath (ORS) extends from the epidermis at the infundibulum and continues to the hair bulb and its cells change considerably throughout the follicle. In the infundibulum, it resembles epidermis, whereas in the isthmus level, ORS cells begin to keratinize in a trichilemmal mode. Keratinocytes in the ORS form the bulge area at the base of the isthmus.
Other immune privileged sites include the anterior chamber of the eye, testis, brain and placenta. Hair follicle IP has a unique characteristic of recurring in a cyclic pattern. The hair follicle is responsible for the production, growth and maintenance of hair. The sebaceous gland produces sebum, or oil, which is the body’s natural conditioner.
The bulge area is located in the middle part (also known as the isthmus) of the hair follicle. It contains stem cells that divide and regenerate not only new hair follicles but the sebaceous glands and the epidermis, too. Wherever you have hair on your body, you also have hair follicles.
During the first few months of infancy there grow fine, short, unpigmented hairs called down hair, or vellus. Vellus covers every part of the body except the palms of the hands, the soles of the feet, undersurfaces of the fingers and toes, and a few other places. The hairs of the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes are of separate types from these others and develop fairly early in life. On the scalp, where hair is usually densest and longest, the average total number of hairs is between 100,000 and 150,000. Human hair grows at a rate of about 0.5 inch (13 mm) per month. The telogen stage is defined as the duration between the completion of follicular regression and the onset of the next anagen phase.

No comments:
Post a Comment